(Default content of this page. This content will be deleted before final submission.)
Entrepreneurship
The entrepreneurship prize recognizes exceptional effort to build a business case and commercialize an iGEM project.
Best Supporting Entrepreneurship
The Best Supporting Entrepreneurship award recognizes exceptional effort to build a business case and commercialize an iGEM project. This award is open to all teams to show that entrepreneurship is something all teams can aspire to do with their project. This award can go to an new project, or to a previous project that a team aimed to commercialize. Have you filed a provisional patent on your project/device/process? Have you raised money to build and ship products? Have you pitched your idea to investors and received money? As always in iGEM, the aim is to impress the judges!
To compete for the Best Supporting Entrepreneurship prize, please describe your work on this page and also fill out the description on the judging form.
Please see the 2023 Awards Page for more information.
Patents and intellectual property
If your team is seriously considering commercializing and looking into building a company after the competition, you may want to look at how you are going to protect your work and secure investment. Investors will usually require some form of intellectual protection, so you may want to investigate how to apply for a patent or provisional patent in your country and region before disclosing your project at iGEM. Remember that you can only be evaluated in iGEM based on what you share on your wiki and at the Jamboree, so any work you don't present can't count towards your project.
This is an area where we are different as we care about sharing, openness and contributing to the community and investors don't always agree with these values. It is up to you and your team to decide what to do. Remember that most universities have a commercialization department and that you can talk to them before coming to a decision.
Introduction
Nowadays, there is a sharply rising consumer demand for vegetable preservation, and plastic wrap is widely employed as a convenient, quick, and effective method. However, there are unmet needs in this space. Despite the low cost of PVC and other materials, plastic wrap usage is prevalent in many developing countries. Unfortunately, it may not only contain harmful additives like DEHA, detrimental to human health, but also, as a composite material, it is often challenging to biodegrade or occur naturally.
To address these concerns and meet the evolving needs of consumers, we have developed a synthetic biological approach to preservation. This innovative method utilizes Escherichia coli bacteria as substrates to produce edible antimicrobial compounds. These compounds are then combined with abundant, edible natural polymers. This pioneering approach will lead to the creation of organic food preservatives that can be easily applied through soaking and spraying. What's more, the resulting product is virtually imperceptible as it is colorless, odorless, and harmless.
Positioned as a first-generation product, we believe there is ample room for further innovation. Our solution not only proves effective for fruits and vegetables but holds the potential to extend its benefits to meats and various other food items in the future. By adopting our approach, consumers can enjoy the benefits of extended food shelf life without the concerns associated with traditional plastic wraps.
Global Importance
Plastic clingfilm is widely utilized for food preservation due to its lightweight and cost-effective nature. Currently, PVC and PE materials dominate the global plastic packaging landscape, posing challenges as they are difficult to degrade naturally, leading to environmental pollution when mishandled. PVC, especially prevalent in developing countries due to its affordability, often incorporates DEHA as a stabilizing plasticizer. However, DEHA can be irritating, and prolonged exposure may disrupt human hormone secretion. There is a clear need for a naturally degradable, environmentally friendly food preservation technique that ensures the safety of human consumption, aiming to address the environmental pollution and health concerns associated with traditional plastic wrap.
Presently, the public perception and utilization of food preservation methods, with plastic wrap being the primary choice, remain relatively uniform. For fruit and vegetable sellers, preservation techniques are categorized based on the food type. Common methods include freezing preservation, but these come with significant energy consumption and high maintenance costs.
Our product targets a specific demographic, namely small fruit and vegetable sellers. It offers excellent preservation properties, extending the freshness of food, while its degradable nature significantly reduces processing costs. The exceptionally low manufacturing costs make it a viable solution for both general consumers and individual traders. Therefore, the introduction of an environmentally friendly, organic, and cost-effective food preservation technique is imperative in addressing the needs of this market segment.
Our Solution
We use antimicrobial peptides to protect fruits and vegetables from microorganisms. Antimicrobial peptides act on and interact with bacterial cell membranes through their hydrophobicity and special structure. Once antimicrobial peptides bind to bacterial cell membranes, they form pores or channels that cause cell membrane destruction. The destruction of the cell membrane creates an imbalance in the balance of ions inside and outside the cell, resulting in osmotic pressure inside the cell and ultimately cell death.
We first constructed recombinant expression strains and transferred the plasmids into the cells. The recombinant strain was induced to express antimicrobial peptides by the addition of the inducer IPTG. After expression validation, the peptide was purified, and the impurity protein was washed off using nickel affinity chromatography with cleavage bacteria. For the silk solution part, we first remove the sericin from the silk and then dissolve the deglutinated silk at 70C..After dialysis, the supernatant was mixed with antibacterial peptide to get silk protein preservation solution. The whole process takes about five days.
In the preparation of antimicrobial peptides, we used the recombinant expression method. Compared with chemical synthesis, recombinant expression has different properties. Chemical synthesis is a common method for preparing small peptides. As the amount of residues increases, synthesis efficiency and cost often become limiting factors. Even for relatively short AMPs, 15N- and 13C- labeled samples for NMR experiments are difficult to obtain by chemical synthesis. Recombinant expression is an effective way to address these issues and is also necessary for the large-scale production of biologically active peptides.
At the level of edible natural polymers, we chose silk protein as the material. More specifically, it is a fibroin protein because it can form a stable protein structure after drying. In terms of material cost, it has the advantage of being cheap and easy to prepare.


SWOT

S: Our products are eco-friendly, edible and naturally degradable compared to plastic wrap. Easily manufactured and relatively inexpensive.
W: The manufacturing cost is slightly higher; the manufacturing process is more complicated and the environmental conditions for production are higher compared to the common plastic wrap on the market. There are also possible unknown risks.
O: Our products have the potential to be promoted due to higher consumer demand for preservation and the support policies.
T: The public is still afraid of biological products and some people will not accept such products. We do not yet know whether the stability of antimicrobial peptides and silk proteins changes over time. It has not been ruled out that some people may be allergic to the silk protein. The way our products are produced may not be compatible with the old system.
The Investigation
For Customer
Customer Investigation Report on Shanghai Citizens' Daily Demand for Fruits and Vegetables
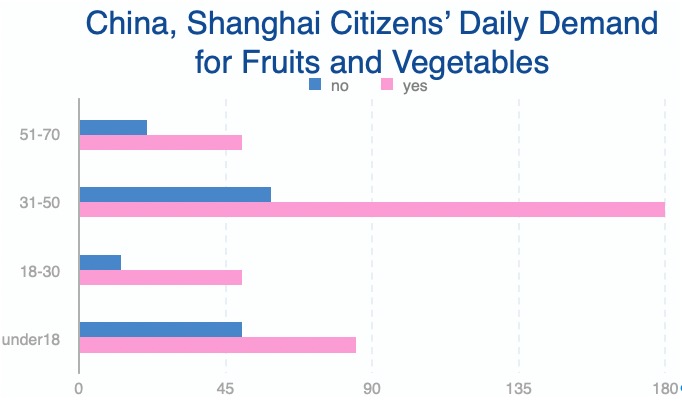
Respondents across all age groups have expressed a substantial demand for fruits and vegetables, with a particularly high emphasis noted among middle-aged individuals (31 to 50 years old).
Daily consumption of fruit
Individual daily fruit consumption varies based on personal eating habits, nutritional needs, cultural influences, and geographical distinctions. In accordance with global health guidelines from organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), adults are recommended to consume approximately 400 grams of vegetables and fruits daily. This recommendation encompasses the total intake of both vegetables and fruits, emphasizing diversity in fruit choices like apples, bananas, oranges, grapes, strawberries, watermelons, etc. Meeting the daily recommended intake ensures a well-rounded nutritional profile. Personal preferences, dietary habits, and health conditions influence the types and quantities of fruits individuals choose to consume.
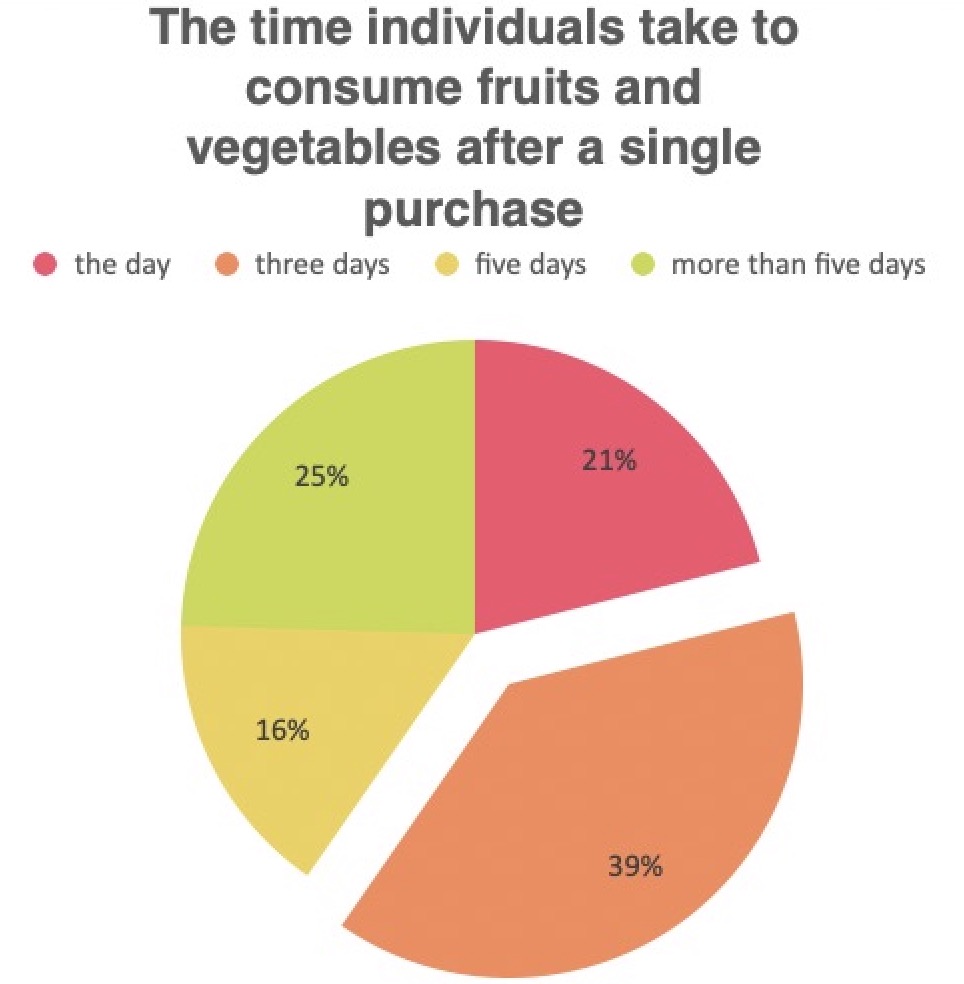
The Final Treatment of Purchased Fruits and Vegetables by Consumers
Identifying Bad Situation: Fruit Rot
Fruit rot manifests through several stages:
- Discoloration and softening, resulting in a loss of the original appearance and texture.
- Growth of bacteria, mold, and yeast on the fruit's surface, forming mildew spots.
- Release of liquid and further liquification.
- Fermentation, leading to the production of volatile substances such as alcohol.
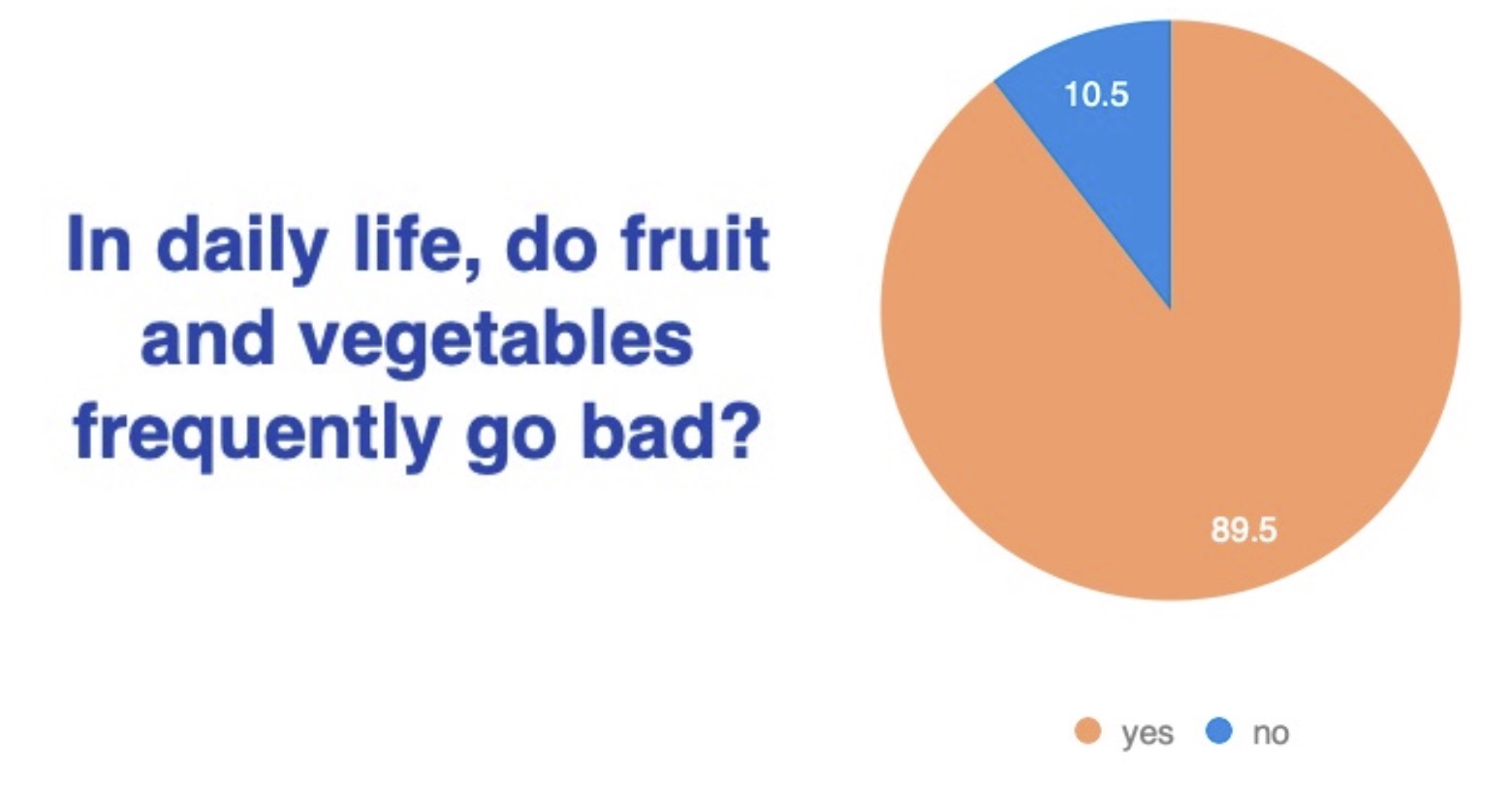
A significant observation reveals that nearly 90 percent of respondents frequently encounter situations where fruits and vegetables decay in their daily lives. The disposal occurs when these items become stale, inedible, or eventually liquid due to factors like damage, overripening, improper storage, microbial infection, or prolonged exposure to environmental conditions.
(The extent to which fruits and vegetables are thrown away is when they become stale, inedible and eventually liquid or rot completely due to damage, overripening, improper storage, microbial infection or prolonged exposure to environmental conditions)
Data Analyze
Based on the sentences provided, it is clear that the vast majority of people, nearly 90% of respondents, often encounter spoiled fruits and vegetables in their daily lives. The findings highlight a widespread problem of food waste and the challenges individuals face in maintaining the freshness and longevity of the fruits and vegetables they purchase.
There are several factors that can contribute to this common problem. First, inadequate storage conditions can be a key factor. Improper storage, such as exposure to different temperatures or inadequate refrigeration, can accelerate the deterioration of fruits and vegetables. In addition, lack of awareness of proper storage techniques or the best shelf life of different agricultural products can also lead to higher waste rates.
In addition, the busy modern lifestyle also plays a role. People with tight schedules can have a hard time planning their meals effectively, leading to an excess of fruits and vegetables that can't be eaten before they go bad. This problem can be exacerbated by buying habits, where people buy in bulk because of convenience or discounts, without considering their actual consumption needs.
The solution to this problem requires a multifaceted approach. Now, our team is focusing on fruit and vegetable preservation technology, which will greatly reduce the occurrence of fruit and vegetable waste in daily life.
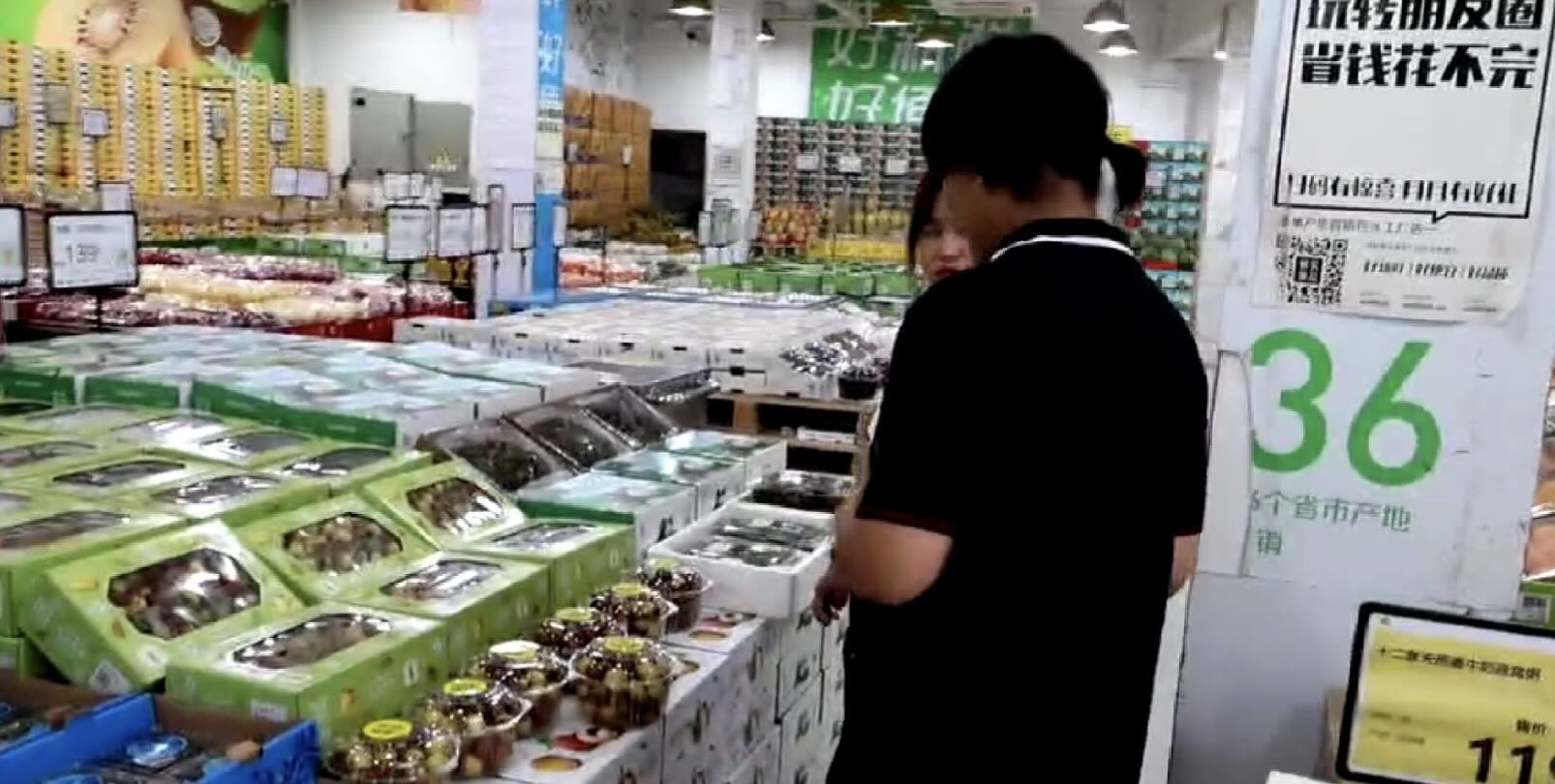
For Merchants
We Interviewed the owner of the fruit and vegetable stores.
The size and sales volume of a fruit store can vary significantly based on location, business model, customer base, and various other factors.
A "mom and dad" corner fruit shop typically refer to a small, independently owned and operated business, often managed by a family. Here's a general overview:
1. Size/Square Feet: Mom and dad corner fruit shops are usually small-scale operations, typically ranging from a few hundred to a couple of thousand square feet. The exact size about 100 square feet.
2. Sales Volume: The sales volume can vary greatly based on the shop's location, the variety and quality of fruits offered, pricing, and customer traffic. It could range from a few hundred dollars per day to several thousand or more per week, depending on the factors mentioned.
3. Peak Season: Peak season for a fruit store often coincides with the harvest seasons for popular fruits in the region. This is when sales and customer traffic are typically higher due to the availability of fresh, locally sourced fruits.
4. Off-Peak/Weak Season: The off-peak or weak season can vary depending on the types of fruits being sold and the location of the shop. During these times, sales may decrease due to factors such as seasonal changes, lower fruit availability, or reduced customer demand.
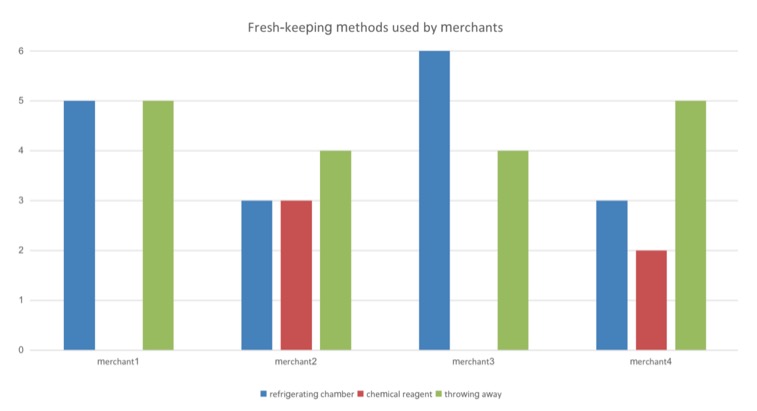
The unit of Y-axis is 1=10kg.
Data analyze
In contemporary times, fruit and vegetable stores employ various methods to maintain the freshness and quality of their products. These methods are essential to extending the shelf life of fruits and vegetables, minimizing waste, and providing customers with high-quality, nutrient-rich products. However, these preservation methods also have some challenges.
Method 1: Freezer
The challenge: Maintaining precise temperature and humidity levels is critical; Improper control can lead to freezing or accelerated deterioration.
Method two: Chemical reagents
The challenge: The chemical preservatives used in fruits and vegetables have their own inherent drawbacks. First, they may introduce harmful substances into agricultural products, posing a health risk when consumed. In addition, these preservatives may alter the taste, texture and nutritional value of fruits and vegetables, affecting their natural qualities and making them less attractive to consumers. Excessive reliance on chemical preservatives can hinder sustainable and eco-friendly practices in agriculture and food storage. In addition, there is growing concern about the health effects of long-term exposure to various preservatives, urging people to switch to more natural and organic alternatives to preserve fruits and vegetables.
Method 3: Discard
Challenges: There are a number of drawbacks that can occur when produce suppliers simply throw away spoiled fruits and vegetables. First, it creates food waste, exacerbating the problem of global resource waste and environmental stress. Moreover, it represents an economic loss for suppliers, affecting their profitability.
COST
Material cost:
Nisin: 100g 6.86$,Natural silk:100g 3.84$
Input equipment cost:
Dialysis machine 4114.56$,Centrifugal machine:13715.2$
Time cost on production: 5 days
Yield: 5wt% silk protein solution 1L.
It is necessary to master the special process of protein purification and antimicrobial peptide culture, so the labor cost is relatively high at present.
FUNDING
Funding Proposal for Antimicrobial Peptide Project:
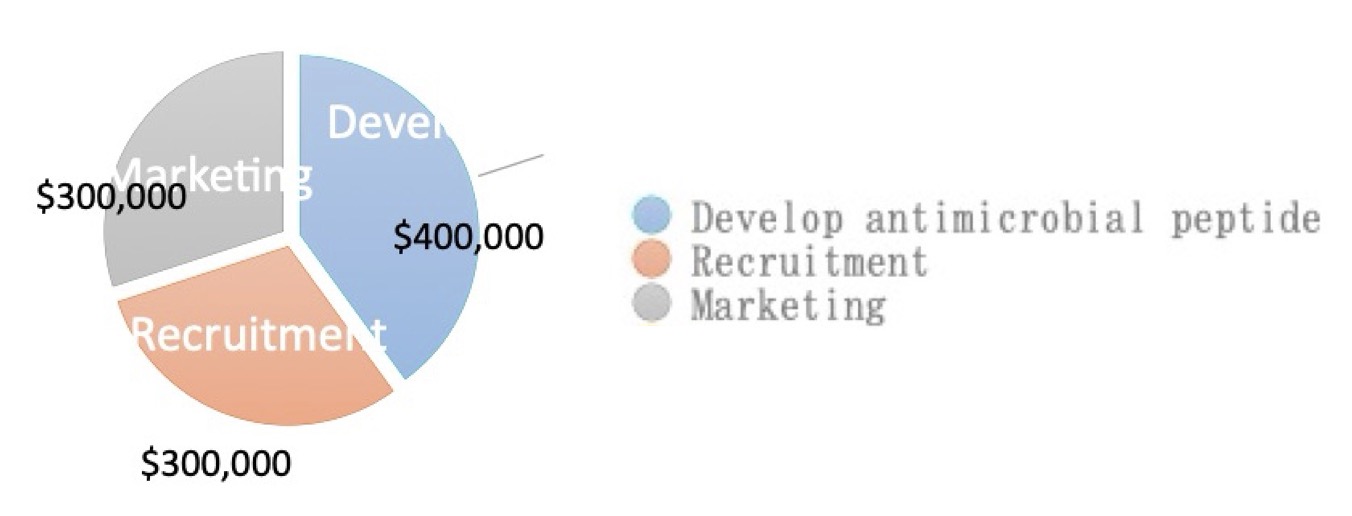
Total Funding Required: $1 Million
Allocation of Funds:
Research and Development (R&D): $400,000
We start by allocating funds for patent applications to safeguard intellectual property. The next step is to Invest in developing enhanced antimicrobial peptides, reducing production costs, and extending antimicrobial properties, complete the silk fibroin production and peptide enhancement. Taking into account the need for equipment and materials, the purchases of necessary instruments, equipment, and raw materials for protein production and culture enhancement will be included. The investment in laboratory renovation and equipment installation will be synchronized.
Talent Recruitment: $300,000
The talent recruitment in genetic engineering is the main expenditures. We will also recruit talents from other departments by utilizing online and offline recruitment channels, including websites, apps, and talent markets. Then, we may explore collaboration opportunities with universities and other biological organizations to secure additional talent resources, providing financial support for recruited talents and research teams.
Marketing Operation Costs: $300,000
Firstly, the funds will be allocated for building connections within the food industry to ensure effective product placement. So that we can identify suitable sites for factories, either through purchase or lease. Otherwise, our products may cause retention. Aim to open various distribution channels, we will establish online sales channels, including website development and e-commerce platforms, exploring opportunities to sell products through platforms like Amazon and establishing official websites. About the offline sales, we could connect with supermarkets and retailers to secure shelf space for the products. For promotions, some of the funds will be used in marketing activities, such as advertising and promotional campaigns. Meanwhile, the funds wil also be utilized for acquiring authoritative certifications can create the compliance to ensure all activities comply with regulatory requirements.
Project Timeline:
Months 1-3: Patent applications and initial R&D activities.
Months 4-6: Protein production and peptide enhancement research.
Months 7-9: Equipment and laboratory infrastructure setup.
Months 10-12: Talent recruitment and collaboration establishment.
Months 13-15: Marketing strategy development and industry outreach.
Months 16-18: Factory site identification and online sales channel setup.
Months 19-24: Full-scale marketing, sales initiation, and compliance adherence.
Expected Outcomes:
Development Plan
1. Experimental Stage:
Consider the current state of our product is in the experimental stage, and the first product has applied for relevant patents with legal protection obtained. So, we decide to continue experimental efforts to refine the product based on initial findings.
2. Optimization and Increased Output:
In this stage, our objective is to optimize the product for enhanced performance and increased production output.
To accomplish the objective, we need to ensure stable product quality. Provide trial products to interested companies for cooperation, collecting valuable feedback.
As a result, we can iteratively improve and update the product.
3. Technical and Financial Support:
In order to contact experts, factories, organizations, and investors for technical and financial support. We will collaborate with experts for technical insights and improvements and seek financial support from organizations or investors to facilitate mass production studies. Establishing partnerships with reputable factories for production scalability.
4. Mass Production Planning:
Developing a comprehensive plan for mass production is the core of expansion.
We will devote ourselves in engaging in a full-scale study of mass production processes and collaborate with manufacturing partners to implement efficient production models. The quality control measures will be in place for large-scale production.
5. Collaboration Expansion
We will attempt to expand collaborations with companies for diverse product applications. It means we need to contract with various companies to integrate antimicrobial peptides into different products and safeguard the interests of both parties through transparent agreements.
6. Distribution Channels:
For establishing convenient and widespread distribution channels, the cognitions of the target group's purchasing channels are the indispensable way to consolidate the consumer base. Therefore, we should make efforts to focusing on supermarkets and online platforms. After that, we begin to embark the negotiations of partnerships with companies for consumer platforms to expose our products to the target audiences, such as Amazon and other major shopping platforms. Thus, the availability and quick accessibility of products for consumers can be ensured.
7. Continuous Improvement:
Enter into this stage, we will start to formulate an implement continuous improvement strategy. We will regularly assess and enhance the product based on market and consumer feedback while staying abreast of technological advancements for potential product upgrades. Hence, we could be accessible to maintain flexibility to adapt to evolving market demands.
8. Regulatory Compliance:
In the whole processes of our activities, we must ensure adherence to all regulatory requirements.
We will keep staying informed about relevant regulations in the industry and work closely with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance at all stages of development and production.
9. Marketing and Consumer Outreach:
For sustainable development of our career, we have to implement effective marketing strategies for consumer awareness.
We use the traditional but effective ways to construct our publicity. For instances, developing marketing campaigns to educate consumers about the benefits of the antimicrobial peptide product and leverage online and offline channels for promotional activities. We emphasis through transparent communication to foster positive relationships with consumers to build our credibility and impression.
We try to make the development plan being comprehensive so that it can outlines the stepwise progression from the experimental stage to full-scale production, emphasizing optimization, collaboration, distribution, continuous improvement, regulatory compliance, and effective marketing. We hope it can contribute our product to expand further.
It is worth mentioning that one of the shop owners made it clear that he is willing to try the product as long as the food safety is ensured.

Challenges
We may be faced with the potential resistance from consumers who may be apprehensive about genetically modified products, the customers also may hold a perception that biological products can't replace traditional methods. Therefore, building and maintaining a loyal consumer base in the face of initial skepticism is hard. When we ensuring successful collaboration with other enterprises in the food industry, the intense competition from existing players in the preservation industry is also need to be handled.
To address these challenges, we intend to implement transparent communication strategies to educate consumers about the safety and benefits of the product. We can conduct a thorough market analysis, develop strategic partnerships to strengthen market presence while continuously innovating and improve the product to stay ahead of the competition. Through establishing clear communication channels with potential partners to align goals and expectations.
By addressing these challenges head-on, the antimicrobial peptide project can carve out its niche in the food preservation industry and contribute to a sustainable and innovative future.